Europe Venture Capital Market Analysis by Mordor Intelligence
The Europe venture capital market is valued at USD 75.71 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 143.31 billion by 2030, delivering a 13.61% CAGR. Growth is underpinned by the European Investment Fund (EIF) and European Investment Bank (EIB), which have mobilized more than USD 10.8 billion in matched capital designed to extend runways for high-growth companies. Policy-linked incentives embedded in the EU Green Deal and Digital Decade programs are directing unprecedented sums into climate-tech and deep-tech, while the maturation of secondary markets provides a recycling valve that prices assets at 89% of Net Asset Value. Although monetary tightening has compressed late-stage valuations, abundant dry powder, a surge in corporate carve-outs, and the rapid professionalization of regional ecosystems continue to feed early-stage pipelines across the Europe venture capital market. Germany is registering the fastest expansion, yet the United Kingdom remains the continent’s dominant node because it concentrates on repeat founders, legal infrastructure, and global investor network.
Key Report Takeaways
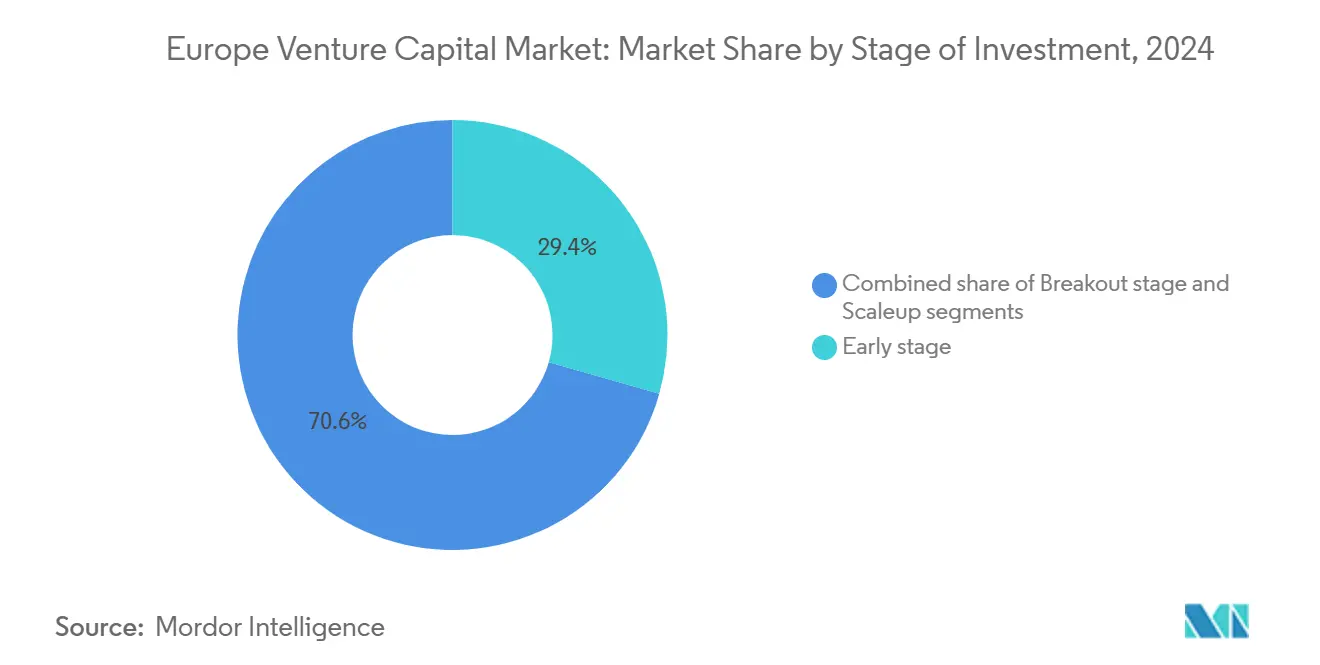
- By stage of investment, early-stage deals held 29.4% of Europe venture capital market share in 2024 and are forecast to grow at an 11.23% CAGR by 2030.
- By industry, fintech led with a 23.3% share of the Europe venture capital market size in 2024, while energy investments are expected to advance at a 14.34% CAGR through 2030.
- By country, the United Kingdom commanded 35.6% of the Europe venture capital market size in 2024; Germany is advancing at a 14.11% CAGR.
- By exit type, strategic M&A accounted for 55.4% of exit value in 2024, whereas secondary sales are rising at a 12.42% CAGR through 2030.
Europe Venture Capital Market Trends and Insights
Drivers Impact Analysis
| Driver | (~ ) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abundant dry-powder supported by EIF & EIB mandates | +2.8% | Pan-European, concentrated in Germany, France, Spain | Medium term (2–4 years) |
| Green & digital-transition incentives under EU Green Deal | +2.1% | EU-wide, strongest in Nordics & Germany | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Maturing hubs producing serial founders in London, Berlin, Paris | +1.9% | United Kingdom, Germany, France | Medium term (2–4 years) |
| Growing secondary VC fund market unlocking LP liquidity | +1.4% | Focus on United Kingdom & Netherlands | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
| Tokenisation of fund shares lowering ticket size for semi-pro investors | +0.8% | France, Netherlands, Luxembourg | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Corporate ESG-driven deep-tech carve-outs creating fundable spin-outs | +1.2% | Germany, France, Italy | Medium term (2–4 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Abundant Dry-Powder Supported by EIF & EIB Mandates
EIF, with commitments like USD 364.5 million to Kembara Fund I and the EIB’s USD 157.5 million AI Co-Investment Facility, is bolstering callable capital for specialized vehicles[1]European Investment Fund, “Behold Ventures Commitment,” eif.org. These investments aim to enhance the availability of funding for innovative projects, particularly in emerging and high-growth sectors. The newly minted USD 183.75 million Defense Equity Facility is poised to unlock USD 525 million by 2027, channeling venture funds into dual-use AI, cybersecurity, and space assets, which are critical for technological advancements and national security. Gender-smart initiatives are pushing for greater founder diversity, especially given that 86% of European VC leadership is male, highlighting the need for more inclusive representation in decision-making roles. Public lenders are extending the average runway from 18 to 24 months. This move is stabilizing the Europe venture capital market amidst valuation compressions, ensuring that startups have the necessary resources to navigate challenging economic conditions and continue their growth trajectories.
Green & Digital-Transition Incentives Under EU Green Deal
Capital channels tied to policy initiatives are speeding up decarbonization efforts. The EIF's investments, including a USD 63 million stake in Future Energy Ventures Fund I and a USD 105 million commitment to Prime Green Energy Infrastructure Fund II, highlight the appeal of Article 9 SFDR structures. These structures, offering concessional terms, have bolstered valuations in Nordic renewable sectors, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Assets with a climate focus now enjoy a 15-20% premium in enterprise value compared to their non-classified counterparts, enticing multi-stage investors to participate in earlier funding rounds. This trend reflects the growing prioritization of sustainability in investment strategies as stakeholders seek to align with global decarbonization goals. Yet, while Western Europe sees a concentration of supply, founders in Central and Eastern Europe face extended due diligence periods, making it challenging to finalize Series B funding. The disparity in regional supply highlights the need for more balanced investment flows to support emerging markets in achieving their climate objectives.
Maturing Hubs Producing Serial Founders in London, Berlin, Paris
In 2024, London-based AI and fintech startups secured over USD 3 billion in equity, buoyed by policy reforms on EMI share options that lessen the tax burden on employees[2]UK Government, “Launch of PISCES Private Share Trading Platform,” gov.uk. These reforms have made it easier for startups to attract and retain top talent, further strengthening their competitive edge. Meanwhile, Berlin and Paris are narrowing the gap, introducing revamped stock-option regimes and strategic talent visas that expedite hiring processes and enhance access to skilled professionals. Notably, in these three cities, 60% of the top-funded Gen-AI firms boast leadership from former Big Tech engineers, empowering founders to negotiate elevated pre-money valuations. This network effect bolsters Europe's venture capital landscape, enabling a seamless transition of successful exits into nurturing the next wave of companies, thereby fostering a robust ecosystem for innovation and growth.
Growing Secondary VC Fund Market Unlocking LP Liquidity
In 2024, global LP secondaries hit USD 87 billion, with European transactions settling at 89% of NAV, presenting an enticing entry discount that benefits sellers. This growth highlights the increasing appeal of LP secondaries as a strategic investment avenue driven by favorable pricing and liquidity opportunities. Isomer Capital has launched a dedicated vehicle with a commitment of USD 105 million, channeling up to 75% of its funds into LP stakes. The remaining portion is directed towards direct secondaries, granting founders liquidity without the need for new governance. These direct secondaries provide a flexible solution for founders seeking capital while maintaining operational control. Continuation funds are now managing seasoned winners, enabling GPs to return cash while extending their hold on top performers. This structural shift bolsters Europe's venture capital market against IPO fluctuations, enhancing its resilience and adaptability in a dynamic financial landscape.
Restraints Impact Analysis
| Restraint | ( ~ ) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monetary tightening raising cost of capital & depressing valuations | −3.2% | Pan-European, most acute in high-growth hubs | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
| Regulatory uncertainty on AI & data (EU AI Act) | −1.8% | EU-wide, notably Germany, France, Netherlands | Medium term (2–4 years) |
| Post-Brexit passporting frictions for UK-based GPs | −1.1% | Cross-border United Kingdom–EU flows | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Specialist-talent scarcity in quantum / deep-tech verticals | −0.9% | United Kingdom, Germany, France | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Monetary Tightening Raising Cost of Capital & Depressing Valuations
In 2024, ECB rate hikes elevated the risk-free baseline and broadened discount-rate spreads, resulting in a roughly 30% dip in pre-money multiples at Series C. While deal counts plummeted by 45.6% year-on-year, venture debt surged, hitting a record USD 4.7 billion[3]European Central Bank, “Monetary Policy Decisions 2024-2025,” ecb.europa.eu. Startups turned to non-dilutive capital, allowing them to sustain operations without jeopardizing their valuations. This trend underscores a cautious stance among investors, many of whom are biding their time for more favorable macroeconomic indicators before diving into new equity rounds. The reliance on venture debt and non-dilutive capital highlights a strategic shift in funding approaches, as startups aim to balance growth with financial stability. Additionally, bridge financing saw a rise: 21.3% of 2024's fundraising took the form of extension rounds, a strategy employed to sidestep down-round perceptions, thereby minimizing cap-table disruptions and safeguarding development timelines. These extension rounds have become a critical tool for startups to maintain investor confidence and ensure continuity in their operations during uncertain market conditions.
Regulatory Uncertainty on AI & Data (EU AI Act)
High-risk systems face costly conformity assessments under the EU AI Act. Compliance tacks on roughly USD 315,000 to validation and demands an additional 6–12 months of engineering time. These challenges hit early-stage startups the hardest, as they often lack both the in-house regulatory know-how and the financial cushion to weather extended go-to-market delays. The Act's intricate classification process has made investors wary of backing cutting-edge AI applications, waiting instead for clearer legal precedents. Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding the classification of AI systems has created a cautious investment environment, slowing the pace of innovation in frontier AI technologies. While open-source exemptions present a strategic advantage, they come with the caveat of rigorous post-market monitoring. This requirement has made generalist funds more cautious, leading them to favor founders with substantial legal budgets and altering the size of their investments. As a result, startups are increasingly forced to allocate resources toward compliance rather than innovation, further compounding the challenges of navigating the regulatory landscape.
Segment Analysis
By Stage of Investment: Early-Stage Dominance Fuels the Pipeline
In 2024, early-stage rounds accounted for 29.4% of Europe's venture capital market share. Projections indicate that the market size for these early-stage investments will grow at a CAGR of 11.23% through 2030, reflecting strong investor interest in this segment. Seed funds, backed by the European Investment Fund (EIF), are prioritizing sectors such as climate tech, artificial intelligence (AI), and life sciences, which are considered high-growth and impactful industries. These funds are focusing on sub-USD 10 million investments, aiming to build diversified portfolios while benefiting from lower entry valuations. This approach mitigates risk and positions investors to capitalize on future growth. Additionally, venture builders like Antler and Entrepreneur First are expanding their operations in cities like Barcelona and Warsaw. These organizations are fostering investor-ready teams, even in cases where traditional angel backing is absent, thereby broadening the pipeline of innovative startups in the region.
Growth-stage transactions are navigating several challenges that are reshaping the dynamics of this segment. Crossover funds, which previously played a significant role, are now managing a reduced number of dedicated EU sleeves, limiting the availability of capital for European growth-stage companies. Furthermore, U.S. comparables continue to trade at higher earnings multiples, which has further narrowed the valuation gap between the two markets. It has made it more challenging for European companies to attract competitive valuations. In response, structured equity instruments, such as convertible loans with valuation caps, have regained relevance as a flexible financing option. These instruments provide companies with access to capital while addressing valuation concerns. Scale-ups are also increasingly relying on “private IPO” mega-secondaries to secure funding. A notable example is Mews’ USD 1.2 billion continuation round, which allowed early angel investors to exit while onboarding late-cycle investors. This trend highlights the evolving strategies employed by scale-ups to navigate funding challenges and sustain their growth trajectories.
Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
By Industry: Fintech Leadership Meets Energy Sector Acceleration
In 2024, fintech captured a 23.3% share of the Europe venture capital market, leveraging PSD2-driven open banking to foster a wave of neo-brokers, reg-techs, and embedded finance models. The implementation of PSD2 has significantly enhanced the financial ecosystem by enabling seamless data sharing and fostering innovation across financial services. It has allowed fintech companies to introduce disruptive business models that cater to evolving consumer demands. Meanwhile, sectors like climate infrastructure, energy storage, and hydrogen are witnessing a robust 14.34% CAGR, drawing the attention of traditionally generalist funds that are now launching thematic climate-focused initiatives. These sectors are benefiting from increasing regulatory support and growing investor interest in sustainable technologies, which are seen as critical to achieving long-term climate goals. However, the fintech sector faces headwinds, grappling with margin compression as revenues from interest-rate-related interchanges stabilize. This normalization of revenues is pressuring fintech firms to explore alternative revenue streams and innovate further to maintain their competitive edge.
Enterprise SaaS consistently outshines risk-adjusted benchmarks due to the pan-European B2B market's preference for local-language customization. The ability to tailor solutions to meet the linguistic and cultural needs of diverse European markets has positioned Enterprise SaaS as a critical enabler of business efficiency and growth. Concurrently, digital health reaps rewards from pilot programs promoting cross-border data sharing, all under the umbrella of the European Health Data Space. These initiatives aim to create a unified framework for health data exchange, improving patient outcomes and fostering innovation in healthcare delivery. Yet, fields like robotics and quantum technology grapple with talent shortages and the challenges of prolonged regulatory compliance. The scarcity of skilled professionals and the complexity of meeting stringent regulatory standards continue to hinder the pace of development in these sectors. Consequently, capital raises in the deep-tech arena frequently combine hybrid grants such as Horizon Europe and the EIC Accelerator with equity to optimize capital efficiency. This approach allows deep-tech companies to mitigate funding risks while advancing their research and development efforts cost-effectively.
By Exit Type: Strategic M&A Prevails, Secondaries Gain Ground
Strategic buyers accounted for 55.4% of Europe venture capital market exit value in 2024, as corporates purchase AI and cybersecurity assets to offset organic R&D gaps. Cross-border IPO liquidity remains muted because fragmented exchanges limit free-float depth, steering founders toward trade sales. Strategic acquisitions also help corporates bridge capability gaps faster than building in-house, especially in time-sensitive tech domains. European industrial giants increasingly rely on M&A pipelines to meet innovation benchmarks and digital transformation targets. In parallel, regulatory complexity in listing regimes discourages IPO planning, reinforcing the appeal of exits via trade buyers.
Secondary solutions accelerate, growing at 12.42% CAGR. Fund-of-fund allocators deploy record sums into continuation vehicles that recycle mature winners. GP-led deals resolve duration mismatch while boosting distributions, a pattern that stabilizes the Europe venture capital market across cycles. These structures provide LPs with optional liquidity without forcing asset liquidation, which is particularly valuable in a high-rate environment. Write-off rates rose modestly, yet protective clauses, liquidation preferences, and anti-dilution softened LP's downside. As underwriting becomes more risk-sensitive, contractual safeguards have emerged as a critical backstop, preserving LP returns and supporting fund resilience.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
Geography Analysis
The United Kingdom’s venture scene remains resilient, aided by the National Wealth Fund and the PISCES platform, which opens private-company share trading to institutional liquidity. London leads AI funding, securing more than USD 3 billion in 2024, and benefits from a pool of 10 fintech unicorns that have seeded 145 spin-offs. However, legal footwork around the Overseas Funds Regime raises fund setup costs and can delay first-close timelines by three months. Germany relishes momentum as its sovereign Climate & Transformation Fund joins forces with KfW to funnel grants and equity into hydrogen, battery materials, and defense AI. The USD 488 million Series C raised by Helsing underscores Berlin’s ability to attract megadeals despite valuation pullbacks.
France is using Bpifrance’s matched-funding model to bolster its Series B and Series C funding rounds, providing critical support to startups during their growth stages. This approach not only enhances access to capital but also strengthens the overall investment ecosystem in the country. Additionally, Paris is benefiting from a streamlined BSPCE stock-option system, which simplifies equity distribution for employees and founders. This regulatory advantage is positioning France as a hub for foreign software entrepreneurs, further driving innovation and competitiveness in the market. In the Nordics, favorable ESG legislation is fostering the development of sustainable investment strategies. Specialized infrastructure managers are leveraging EIF anchors and pension-fund carve-outs to create investment vehicles worth USD 312.4–520.7 million, enabling the region to attract significant capital while aligning with global sustainability goals.
In the Benelux region, pro-tokenization directives aligned with ELTIF 2.0 are transforming Luxembourg and the Netherlands into preferred domiciles for digital-unit funds. These regulatory frameworks are facilitating the growth of tokenized assets, offering investors greater flexibility and transparency. This strategic positioning is helping the Benelux economies punch above their weight in the competitive European investment landscape. Meanwhile, Central & Eastern Europe is utilizing EU cohesion funds to mitigate risks in pre-seed investments, providing a much-needed boost to early-stage startups. However, the region faces challenges due to the lack of robust local secondary markets, which slows down cash realizations and limits liquidity for investors. As a result, founders are increasingly seeking Western co-investors to secure funding for late-stage rounds, highlighting the need for further development of local financial infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape
In the European venture capital landscape, a moderate concentration is evident: the top five managers oversee less than half of the total committed capital. It indicates a relatively balanced distribution of capital among various players, fostering competition and innovation. While CVC, KKR, and EQT lead the pack with their significant market presence, thematic specialists like Atomico, Moonfire, and Revaia are making significant inroads into emerging sectors. These specialists are gaining traction by focusing on niche areas and addressing specific market needs, which positions them as key players in shaping the future of the venture capital market. Their ability to adapt to evolving trends and identify high-growth opportunities within emerging verticals further strengthens their influence in the market.
There is a discernible shift towards sector-specific strategies, reflecting a growing preference for targeted investments. For instance, Atomico's USD 754 million growth fund allocates nearly half of its resources to climate solutions, highlighting the increasing importance of sustainability in investment decisions. Similarly, Schroders' newly launched USD 600 million fund zeroes in on generative AI and biopharma, two rapidly evolving fields with substantial growth potential. These sector-focused approaches demonstrate a strategic alignment with global megatrends, ensuring long-term relevance and impact. Additionally, secondary-focused players like Isomer Capital are emulating U.S. market trends by targeting 65–75% stakes from limited partners. This approach aligns with global best practices and underscores the dynamic nature of the European venture capital market as it adapts to changing investor preferences and market conditions. By adopting such strategies, these players are positioning themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities while maintaining a competitive edge.
Technology adoption is a competitive lever. Managers embrace on-chain cap-table tools to offer monthly NAV marks, which LPs prize in mark-to-market reporting. Tokenized feeder funds slice minimums to below EUR 5,000, allowing wealth-management platforms to plug retail flow into late-stage rounds. GP rotation into defense tech accelerates, with General Catalyst’s USD 4.5 billion venture sleeve leading Helsing’s megadeal. Corporate venture capital (CVC) arms re-emerge: Siemens Energy, BMW i Ventures, and Shell Ventures deploy evergreen pools that co-lead Series B rounds, injecting strategic demand that shores up exit valuations. Family offices, especially Italian industrial dynasties, continue to shift allocations from real estate into the Europe venture capital market, signing co-investment rights alongside mid-cap GPs.
Europe Venture Capital Industry Leaders
-
360 Capital
-
AAC Capital
-
Accel
-
Acton Capital
-
Adara Ventures
- *Disclaimer: Major Players sorted in no particular order

Recent Industry Developments
- May 2025: Schroders closes USD 600 million venture and secondary vehicle focused on generative AI and biopharma.
- May 2025: UK government launches PISCES platform to trade private-company shares, improving liquidity for growth-stage firms.
- February 2025: Bpifrance commits up to USD 27 million to blockchain ventures, entrenching France as a sovereign-fund pioneer in digital assets.
- February 2025: EIF pledges USD 20.9 million to Behold Ventures, a Nordic gaming fund targeting a USD 25.4 billion regional market.
Europe Venture Capital Market Report Scope
Venture capital is a form of private equity financing that is provided by venture capital firms or funds to startups, early-stage, and emerging companies that have been deemed to have high growth potential or which have demonstrated high growth.
A complete background analysis of the Europe venture capital market, which includes an assessment of the parental market, emerging trends by segments, and regional markets. Significant changes in market dynamics and market overview are also covered in the report.
The Europe Venture Capital Market is segmented by investments in country (UK, Germany, Finland, Spain, and Others), by the size of the deal (angel/seed investing, early-stage investing, and late-stage investing), and by the industry of investment (fintech, pharma & BioTech, consumer goods, industrial/energy, IT hardware & services, and other industries).
| By Stage of Investment | Early stage |
| Breakout stage | |
| Scaleup | |
| By Industry | Health |
| Fintech | |
| Enterprise Software | |
| Energy | |
| Transportation | |
| Robotics | |
| Other Industries | |
| By Exit Type | Initial Public Offering (IPO) |
| Strategic M&A | |
| Secondary Sale/Buy-out | |
| Writeoffs | |
| By Country | United Kingdom |
| Germany | |
| France | |
| Nordics | |
| Benelux |
| Early stage |
| Breakout stage |
| Scaleup |
| Health |
| Fintech |
| Enterprise Software |
| Energy |
| Transportation |
| Robotics |
| Other Industries |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) |
| Strategic M&A |
| Secondary Sale/Buy-out |
| Writeoffs |
| United Kingdom |
| Germany |
| France |
| Nordics |
| Benelux |
Key Questions Answered in the Report
What is the projected CAGR for the Europe venture capital market through 2030?
The market is expected to expand at 13.61% CAGR, rising from USD 75.71 billion in 2025 to USD 143.31 billion in 2030.
Which investment stage is growing fastest?
Early-stage deals are projected to grow at an 11.23% CAGR, retaining the largest share of deal count across the Europe venture capital market.
Why are secondary transactions important in Europe?
They clear at 89% of NAV on average and already represent 20% of global private equity exits, offering LPs faster liquidity while letting GPs hold outperforming assets longer.
How is the EU Green Deal influencing capital flows?
Article 9-compliant funds secure concessional terms, pushing more capital toward climate-tech, renewables, and energy storage ventures.
What are the main regulatory challenges for AI startups in Europe?
The EU AI Act imposes rigorous conformity assessments and technical documentation requirements, adding significant compliance costs and delaying time-to-market for high-risk applications.
Which country is forecast to grow fastest?
Germany leads with a 14.11% CAGR forecast, driven by sovereign investment in industrial AI, defense technology, and deep-tech infrastructure.
Page last updated on: June 30, 2025